Asimudeen Sahabudeen

Description
Hello! I’m a Data Enthusiast with a passion for uncovering insights from raw information and using them to drive decision-making and innovation. What fuels my enthusiasm for data? It’s the thrill of diving deep into datasets, the challenge of transforming complex patterns into understandable insights, and the satisfaction of seeing those insights inform strategic decisions. I believe that in our data-driven world, the ability to interpret and utilize data is not just a skill, but a language that every industry should speak. Beyond my love for data, I’m an adventurer at heart. I’m always on the lookout for new challenges and learning opportunities, whether that’s mastering a new data visualization tool or exploring a new city. View My LinkedIn Profile
A Data driven approach to understand mental health better.
Sicuro Data Analysis — The project is divided into four distinct subparts:
First part of the project focused on data collection. This involved identifying the types of data that needed to be collected to achieve the project’s objectives. Once the data requirements had been established, appropriate methods for collecting, processing, and storing the data were developed. This involved developing data collection protocols, and implementing data management systems.
Second part of the project focused on data analysis. This involved selecting appropriate methods and tools for analyzing the collected data. The analysis have been conducted at different levels, depending on the research questions being addressed. For example, descriptive statistics may have been used to summarize the data, while inferential statistics may have been used to test hypotheses and make predictions for the machine learning stages.
Third part of the project focused on the display of insights. This involved designing an intuitive and user-friendly interface for presenting the results of the data analysis to users. The design of the app took into account the principles of good data visualization and provided users with clear and actionable insights.
Fourth part of the project focused on machine learning. This involved developing and implementing machine learning algorithms to analyze the collected data. Machine learning was used to predict mood and stress levels based on the other data logged by users.
The below consists of part 2-4. Part 1 can be found: https://github.com/Asim-codes/Sicuro_app_code
Initialize firebase
import firebase_admin
from firebase_admin import credentials
cred = credentials.Certificate("serviceAccountKey.json")
firebase_admin.initialize_app(cred)
from firebase_admin import firestore
db = firestore.client()
Getting data from a particular document
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
#insert document ID if needed
data = db.collection("Users").document().get()
if data.exists:
print(data.to_dict())
Creating a test data, and pushing into firebase firestore
#add documents
import datetime
import random
#Age: 25-35
#Work: Finance, Healthcare
#Family: 4-6
#Ethnicity: Chinese or Indian
#Marital Status: Separated, Divorced, Single
#BMI: Under, Obese
#Symptoms: 6-8
#Steps: 0-3000
#Sleep: 4-5
#Education Level: Doctorate, Masters
###########################################
#Mood: Sad
#Stress: High
for i in range(50):
age = random.randint(25, 35)
weight = random.randint(80, 90)
height = random.randint(165, 170)
familyMembers = random.randint(4, 6)
symptoms = random.randint(6, 8)
steps = random.randint(0, 3000)
sleep = random.randint(4, 5)
gender = random.choice(["M", "F"])
ethnicity = random.choice(["Chinese", "Indian"])
maritalStatus = random.choice(["Separated", "Divorced", "Single"])
industry = random.choice(["Finance", "Healthcare"])
educationLevel = random.choice(["Doctorate", "Masters"])
mood_lists = []
stress_lists = []
for i in range(7):
age = random.randint(18, 20)
weight = random.randint(50, 60)
height = random.randint(165, 170)
mood = []
stress = []
previous_date = datetime.datetime.strptime('05/04/2023 at 5:38 PM', '%d/%m/%Y at %I:%M %p')
for j in range(1, 7):
next_date = previous_date + datetime.timedelta(days=1)
mood.append([random.randint(0,2), next_date])
previous_date = next_date
mood_lists.append(mood)
for k in range(1, 7):
next_date = previous_date + datetime.timedelta(days=1)
stress.append([random.randint(8,10), next_date])
previous_date = next_date
stress_lists.append(stress)
formatted_moods = [" ".join([str(int(mood[0])), mood[1].strftime('%d/%m/%Y at %I:%M %p')]) for mood_list in mood_lists for mood in mood_list]
formatted_stress = [" ".join([str(int(stress[0])), stress[1].strftime('%d/%m/%Y at %I:%M %p')]) for stress_list in stress_lists for stress in stress_list]
data = {
'fullName': 'John Doe','gender': gender,
'age': age,'weight': weight,'height': height,
'livingArea': 'U',
'educationLevel': educationLevel,
'industry': industry,
'mentalIllness': 'None',
'familyMembers': familyMembers,
'nationality': 'Chinese',
'ethnicity': ethnicity,
'maritialStatus': maritalStatus,
'mood': formatted_moods,
'stress': formatted_stress,
'BMI' : (weight/height/height)*10000,
'Symptoms': symptoms,
'Steps': steps,
'Sleep': sleep,
'role': 'User'
}
db.collection('Users').add(data)
print('Data added')
::: {.output .stream .stdout} Data added :::
#add documents
import datetime
import random
#Age: 20-25, 35-40
#Work: Student, Aerospace
#Family: random
#Ethnicity: random
#Marital Status: Married, Single, Divorced
#BMI: Overweight, Normal
#Symptoms: 4-6
#Steps: 4000-5000
#Sleep: 6
#Education Level: Bachelors
###########################################
#Mood: Neutral
#Stress: Medium
for i in range(50):
age1 = random.randint(20, 25)
age2 = random.randint(35, 40)
age = random.choice([age1, age2])
weight = random.randint(50, 90)
height = random.randint(165, 170)
familyMembers = random.randint(1, 6)
symptoms = random.randint(4, 6)
steps = random.randint(4000, 5000)
sleep = random.randint(6,6)
gender = random.choice(["M", "F"])
ethnicity = random.choice(["Chinese", "Indian", "Japanese", "Danish"])
maritalStatus = random.choice(["Separated", "Divorced", "Single"])
industry = random.choice(["Student", "Aerospace"])
educationLevel = "Bachelors"
mood_lists = []
stress_lists = []
for i in range(7):
age = random.randint(18, 20)
weight = random.randint(50, 60)
height = random.randint(165, 170)
mood = []
stress = []
previous_date = datetime.datetime.strptime('05/04/2023 at 5:38 PM', '%d/%m/%Y at %I:%M %p')
for j in range(1, 7):
next_date = previous_date + datetime.timedelta(days=1)
mood.append([random.randint(2,3), next_date])
previous_date = next_date
mood_lists.append(mood)
for k in range(1, 7):
next_date = previous_date + datetime.timedelta(days=1)
stress.append([random.randint(4,7), next_date])
previous_date = next_date
stress_lists.append(stress)
formatted_moods = [" ".join([str(int(mood[0])), mood[1].strftime('%d/%m/%Y at %I:%M %p')]) for mood_list in mood_lists for mood in mood_list]
formatted_stress = [" ".join([str(int(stress[0])), stress[1].strftime('%d/%m/%Y at %I:%M %p')]) for stress_list in stress_lists for stress in stress_list]
data = {
'fullName': 'John Doe','gender': gender,
'age': age,'weight': weight,'height': height,
'livingArea': 'U',
'educationLevel': educationLevel,
'industry': industry,
'mentalIllness': 'None',
'familyMembers': familyMembers,
'nationality': 'Chinese',
'ethnicity': ethnicity,
'maritialStatus': maritalStatus,
'mood': formatted_moods,
'stress': formatted_stress,
'BMI' : (weight/height/height)*10000,
'Symptoms': symptoms,
'Steps': steps,
'Sleep': sleep,
'role': 'User'
}
db.collection('Users').add(data)
print('Data added')
::: {.output .stream .stdout} Data added :::
#add documents
import datetime
import random
#Age: 18-20, 40-45
#Work: Technology, F&B
#Family: rand
#Ethnicity: Japanese, Danish
#Marital Status: Widowed, Married
#BMI: Normal
#Symptoms: 1-4
#Steps: 6000-8000
#Sleep: 7-8
#Education Level: Secondary
###########################################
#Mood: Happy
#Stress: Low
for i in range(50):
age1 = random.randint(18,20)
age2 = random.randint(40,45)
age = random.choice([age1,age2])
weight = random.randint(50, 90)
height = random.randint(165, 170)
familyMembers = random.randint(1, 6)
symptoms = random.randint(4, 6)
steps = random.randint(4000, 5000)
sleep = random.randint(7,8)
gender = random.choice(["M", "F"])
ethnicity = random.choice(["Japanese", "Danish"])
maritalStatus = random.choice(["Separated", "Divorced", "Single"])
industry = random.choice(["Technology", "F&B"])
educationLevel = random.choice(["Secondary"])
mood_lists = []
stress_lists = []
for i in range(7):
age = random.randint(18, 20)
weight = random.randint(50, 60)
height = random.randint(165, 170)
mood = []
stress = []
previous_date = datetime.datetime.strptime('05/04/2023 at 5:38 PM', '%d/%m/%Y at %I:%M %p')
for j in range(1, 7):
next_date = previous_date + datetime.timedelta(days=1)
mood.append([random.randint(4,5), next_date])
previous_date = next_date
mood_lists.append(mood)
for k in range(1, 7):
next_date = previous_date + datetime.timedelta(days=1)
stress.append([random.randint(1,3), next_date])
previous_date = next_date
stress_lists.append(stress)
formatted_moods = [" ".join([str(int(mood[0])), mood[1].strftime('%d/%m/%Y at %I:%M %p')]) for mood_list in mood_lists for mood in mood_list]
formatted_stress = [" ".join([str(int(stress[0])), stress[1].strftime('%d/%m/%Y at %I:%M %p')]) for stress_list in stress_lists for stress in stress_list]
data = {
'fullName': 'John Doe','gender': gender,
'age': age,'weight': weight,'height': height,
'livingArea': 'U',
'educationLevel': educationLevel,
'industry': industry,
'mentalIllness': 'None',
'familyMembers': familyMembers,
'nationality': 'Chinese',
'ethnicity': ethnicity,
'maritialStatus': maritalStatus,
'mood': formatted_moods,
'stress': formatted_stress,
'BMI' : (weight/height/height)*10000,
'Symptoms': symptoms,
'Steps': steps,
'Sleep': sleep,
'role': 'User'
}
db.collection('Users').add(data)
print('Data added')
::: {.output .stream .stdout} Data added :::
Getting data from all the documents in a collection
docs = db.collection("Users").get()
data = []
for doc in docs:
data.append(doc.to_dict())
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
print(df.head(5))
::: {.output .stream .stdout}
age stress nationality
0 20 [1 12/04/2023 at 05:38 PM, 1 13/04/2023 at 05:… Chinese
1 20 [9 12/04/2023 at 05:38 PM, 8 13/04/2023 at 05:… Chinese
2 20 [3 12/04/2023 at 05:38 PM, 2 13/04/2023 at 05:… Chinese
3 18 [6 12/04/2023 at 05:38 PM, 4 13/04/2023 at 05:… Chinese
4 18 [10 12/04/2023 at 05:38 PM, 8 13/04/2023 at 05… Chinese
Symptoms mood Steps \
0 4 [4 06/04/2023 at 05:38 PM, 5 07/04/2023 at 05:... 4619
1 7 [2 06/04/2023 at 05:38 PM, 1 07/04/2023 at 05:... 979
2 5 [5 06/04/2023 at 05:38 PM, 4 07/04/2023 at 05:... 4196
3 4 [2 06/04/2023 at 05:38 PM, 3 07/04/2023 at 05:... 4667
4 8 [1 06/04/2023 at 05:38 PM, 2 07/04/2023 at 05:... 2647
ethnicity livingArea maritialStatus Sleep height educationLevel \
0 Japanese U Separated 8 166 Secondary
1 Indian U Separated 5 167 Doctorate
2 Japanese U Single 7 170 Secondary
3 Chinese U Separated 6 168 Bachelors
4 Indian U Divorced 5 165 Doctorate
industry fullName mentalIllness role familyMembers gender BMI \
0 Technology John Doe None User 5 M 18.144869
1 Finance John Doe None User 5 M 18.286780
2 F&B John Doe None User 1 F 18.685121
3 Aerospace John Doe None User 5 F 21.258503
4 Healthcare John Doe None User 4 M 18.732782
weight
0 50
1 51
2 54
3 60
4 51 ::: :::
Checking datatypes
print(df.dtypes)
::: {.output .stream .stdout} age int64 stress object nationality object Symptoms int64 mood object Steps int64 ethnicity object livingArea object maritialStatus object Sleep int64 height int64 educationLevel object industry object fullName object mentalIllness object role object familyMembers int64 gender object BMI float64 weight int64 dtype: object ::: :::
Pre-processing
Extracting the mood numbers and storing it in an array
# define a lambda function to extract the first number from each string in a list object
extract_first_numbers = lambda x: [int(str(x).split()[0]) if isinstance(x, str) else x for x in x]
# apply the lambda function to each value in the 'mood' column
updated_mood = df['mood'].apply(extract_first_numbers)
# update the 'mood' column in the DataFrame with the updated_mood series
df['mood'] = updated_mood
# print updated DataFrame
print(df['mood'].head())
::: {.output .stream .stdout} 0 [4, 5, 4, 4, 5, 4, 5, 5, 4, 4, 5, 5, 5, 4, 4, … 1 [2, 1, 0, 0, 0, 2, 2, 1, 2, 2, 2, 0, 1, 1, 2, … 2 [5, 4, 4, 5, 5, 5, 5, 4, 4, 5, 5, 5, 5, 5, 5, … 3 [2, 3, 3, 2, 2, 2, 3, 3, 3, 3, 3, 2, 2, 3, 3, … 4 [1, 2, 1, 0, 1, 2, 2, 2, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 2, 2, … Name: mood, dtype: object :::
Extracting the stress numbers and storing it in an array
# define a lambda function to extract the first number from each string in a list object
extract_first_numbers = lambda x: [int(str(x).split()[0]) if isinstance(x, str) else x for x in x]
# apply the lambda function to each value in the 'mood' column
updated_stress = df['stress'].apply(extract_first_numbers)
# update the 'mood' column in the DataFrame with the updated_mood series
df['stress'] = updated_stress
# print updated DataFrame
print(df['stress'].head())
::: {.output .stream .stdout} 0 [1, 1, 3, 3, 1, 1, 1, 1, 2, 3, 3, 2, 2, 3, 1, … 1 [9, 8, 10, 8, 9, 10, 8, 9, 10, 8, 9, 10, 8, 10… 2 [3, 2, 2, 2, 1, 3, 3, 1, 3, 2, 3, 2, 1, 1, 1, … 3 [6, 4, 5, 4, 6, 7, 6, 4, 6, 7, 6, 7, 7, 6, 6, … 4 [10, 8, 9, 8, 9, 8, 9, 8, 10, 9, 9, 9, 8, 9, 8… Name: stress, dtype: object ::: :::
Checking the number of data in the database
print(df.shape)
::: {.output .stream .stdout} (450, 20) :::
Putting all numeric data in one data frame
# remove non-numeric columns
df_numeric = df.drop(['educationLevel', 'industry', 'fullName', 'role', 'ethnicity','nationality' , 'maritialStatus' , 'mentalIllness', 'livingArea', 'gender'], axis=1)
print(df_numeric.head())
::: {.output .stream .stdout}
age stress Symptoms
0 20 [1, 1, 3, 3, 1, 1, 1, 1, 2, 3, 3, 2, 2, 3, 1, … 4
1 20 [9, 8, 10, 8, 9, 10, 8, 9, 10, 8, 9, 10, 8, 10… 7
2 20 [3, 2, 2, 2, 1, 3, 3, 1, 3, 2, 3, 2, 1, 1, 1, … 5
3 18 [6, 4, 5, 4, 6, 7, 6, 4, 6, 7, 6, 7, 7, 6, 6, … 4
4 18 [10, 8, 9, 8, 9, 8, 9, 8, 10, 9, 9, 9, 8, 9, 8… 8
mood Steps Sleep height \
0 [4, 5, 4, 4, 5, 4, 5, 5, 4, 4, 5, 5, 5, 4, 4, ... 4619 8 166
1 [2, 1, 0, 0, 0, 2, 2, 1, 2, 2, 2, 0, 1, 1, 2, ... 979 5 167
2 [5, 4, 4, 5, 5, 5, 5, 4, 4, 5, 5, 5, 5, 5, 5, ... 4196 7 170
3 [2, 3, 3, 2, 2, 2, 3, 3, 3, 3, 3, 2, 2, 3, 3, ... 4667 6 168
4 [1, 2, 1, 0, 1, 2, 2, 2, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 2, 2, ... 2647 5 165
familyMembers BMI weight
0 5 18.144869 50
1 5 18.286780 51
2 1 18.685121 54
3 5 21.258503 60
4 4 18.732782 51 :::
Putting non-numeric data in one data frame
df_non_numeric =df.drop(['fullName','age', 'stress', 'Symptoms', 'mood', 'Steps', 'Sleep', 'height', 'weight', 'familyMembers', 'BMI'], axis = 1)
print(df_non_numeric[['educationLevel', 'maritialStatus']])
::: {.output .stream .stdout} educationLevel maritialStatus 0 Secondary Separated 1 Doctorate Separated 2 Secondary Single 3 Bachelors Separated 4 Doctorate Divorced .. … … 445 Secondary Separated 446 Secondary Separated 447 Masters Divorced 448 Secondary Single 449 Doctorate Separated
[450 rows x 2 columns] :::
Label encoding
from sklearn.preprocessing import LabelEncoder
# create a label encoder object
le = LabelEncoder()
# encode the 'educationLevel' column
df_numeric['educationLevel_encoded'] = le.fit_transform(df['educationLevel'])
print(df_numeric[['educationLevel_encoded']])
::: {.output .stream .stdout} educationLevel_encoded 0 3 1 1 2 3 3 0 4 1 .. … 445 3 446 3 447 2 448 3 449 1
[450 rows x 1 columns] ::: :::
One-hot encoding
import pandas as pd
# create a new DataFrame with the categorical columns
df_cat = df[['gender', 'industry', 'ethnicity' , 'nationality' , 'mentalIllness' , 'livingArea']]
# one-hot encode the categorical columns
df_cat_encoded = pd.get_dummies(df_cat)
# concatenate the one-hot encoded columns with the original DataFrame
df_encoded = pd.concat([df_numeric, df_cat_encoded], axis=1)
print(df_encoded.head())
#for col in df_encoded.columns:
# print("'",col,"'", ",")
::: {.output .stream .stdout}
age stress Symptoms
0 20 [1, 1, 3, 3, 1, 1, 1, 1, 2, 3, 3, 2, 2, 3, 1, … 4
1 20 [9, 8, 10, 8, 9, 10, 8, 9, 10, 8, 9, 10, 8, 10… 7
2 20 [3, 2, 2, 2, 1, 3, 3, 1, 3, 2, 3, 2, 1, 1, 1, … 5
3 18 [6, 4, 5, 4, 6, 7, 6, 4, 6, 7, 6, 7, 7, 6, 6, … 4
4 18 [10, 8, 9, 8, 9, 8, 9, 8, 10, 9, 9, 9, 8, 9, 8… 8
mood Steps Sleep height \
0 [4, 5, 4, 4, 5, 4, 5, 5, 4, 4, 5, 5, 5, 4, 4, ... 4619 8 166
1 [2, 1, 0, 0, 0, 2, 2, 1, 2, 2, 2, 0, 1, 1, 2, ... 979 5 167
2 [5, 4, 4, 5, 5, 5, 5, 4, 4, 5, 5, 5, 5, 5, 5, ... 4196 7 170
3 [2, 3, 3, 2, 2, 2, 3, 3, 3, 3, 3, 2, 2, 3, 3, ... 4667 6 168
4 [1, 2, 1, 0, 1, 2, 2, 2, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 2, 2, ... 2647 5 165
familyMembers BMI weight ... industry_Healthcare \
0 5 18.144869 50 ... 0
1 5 18.286780 51 ... 0
2 1 18.685121 54 ... 0
3 5 21.258503 60 ... 0
4 4 18.732782 51 ... 1
industry_Student industry_Technology ethnicity_Chinese ethnicity_Danish \
0 0 1 0 0
1 0 0 0 0
2 0 0 0 0
3 0 0 1 0
4 0 0 0 0
ethnicity_Indian ethnicity_Japanese nationality_Chinese \
0 0 1 1
1 1 0 1
2 0 1 1
3 0 0 1
4 1 0 1
mentalIllness_None livingArea_U
0 1 1
1 1 1
2 1 1
3 1 1
4 1 1
[5 rows x 26 columns] :::
Combining both encoding
import pandas as pd
from sklearn.preprocessing import LabelEncoder
# Create a label encoder object
le = LabelEncoder()
# Create a new DataFrame with the categorical columns
df_cat = df[['gender', 'industry', 'ethnicity', 'nationality', 'mentalIllness', 'livingArea']]
# One-hot encode the categorical columns
df_cat_encoded = pd.get_dummies(df_cat)
# Combine the numeric columns, the one-hot encoded columns and 'educationLevelEncoded' column into a single DataFrame
df_encoded = pd.concat([df_numeric, df_cat_encoded], axis=1)
# Print the first few rows of the updated DataFrame
print(df_encoded.head())
::: {.output .stream .stdout}
age stress Symptoms
0 20 [1, 1, 3, 3, 1, 1, 1, 1, 2, 3, 3, 2, 2, 3, 1, … 4
1 20 [9, 8, 10, 8, 9, 10, 8, 9, 10, 8, 9, 10, 8, 10… 7
2 20 [3, 2, 2, 2, 1, 3, 3, 1, 3, 2, 3, 2, 1, 1, 1, … 5
3 18 [6, 4, 5, 4, 6, 7, 6, 4, 6, 7, 6, 7, 7, 6, 6, … 4
4 18 [10, 8, 9, 8, 9, 8, 9, 8, 10, 9, 9, 9, 8, 9, 8… 8
mood Steps Sleep height \
0 [4, 5, 4, 4, 5, 4, 5, 5, 4, 4, 5, 5, 5, 4, 4, ... 4619 8 166
1 [2, 1, 0, 0, 0, 2, 2, 1, 2, 2, 2, 0, 1, 1, 2, ... 979 5 167
2 [5, 4, 4, 5, 5, 5, 5, 4, 4, 5, 5, 5, 5, 5, 5, ... 4196 7 170
3 [2, 3, 3, 2, 2, 2, 3, 3, 3, 3, 3, 2, 2, 3, 3, ... 4667 6 168
4 [1, 2, 1, 0, 1, 2, 2, 2, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 2, 2, ... 2647 5 165
familyMembers BMI weight ... industry_Healthcare \
0 5 18.144869 50 ... 0
1 5 18.286780 51 ... 0
2 1 18.685121 54 ... 0
3 5 21.258503 60 ... 0
4 4 18.732782 51 ... 1
industry_Student industry_Technology ethnicity_Chinese ethnicity_Danish \
0 0 1 0 0
1 0 0 0 0
2 0 0 0 0
3 0 0 1 0
4 0 0 0 0
ethnicity_Indian ethnicity_Japanese nationality_Chinese \
0 0 1 1
1 1 0 1
2 0 1 1
3 0 0 1
4 1 0 1
mentalIllness_None livingArea_U
0 1 1
1 1 1
2 1 1
3 1 1
4 1 1
[5 rows x 26 columns] :::
Function to categorize correlations
def categorize_correlation(correlation):
if correlation >= 0.9:
return "Very strongly positive"
elif correlation >= 0.7:
return "Strongly positive"
elif correlation >= 0.5:
return "Moderately positive"
elif correlation >= 0.3:
return "Weakly positive"
elif correlation > -0.3 and correlation < 0.3:
return "No correlation"
elif correlation <= -0.3 and correlation > -0.5:
return "Weakly negative"
elif correlation <= -0.5 and correlation > -0.7:
return "Moderately negative"
elif correlation <= -0.7 and correlation > -0.9:
return "Strongly negative"
else:
return "Very strongly negative"
Computing correlation matrix
# Convert columns to numeric data types
df_numeric['height'] = pd.to_numeric(df_numeric['height'])
df_numeric['weight'] = pd.to_numeric(df_numeric['weight'])
df_numeric['mood_avg'] = df_numeric['mood'].apply(lambda x: np.mean(x))
df_numeric['stress_avg'] = df_numeric['stress'].apply(lambda x: np.mean(x))
df_numeric['familyMembers'] = pd.to_numeric(df_numeric['familyMembers'])
#df_numeric['severityLevel'] = df_numeric['severityLevel'].apply(pd.to_numeric, errors='coerce')
# Check the data types of all columns in df_numeric
#print(df_numeric.dtypes)
# Compute correlation matrix
corr_matrix = df_numeric.corr()
corr_categories = corr_matrix.applymap(categorize_correlation)
print(df_numeric.describe())
#print(df_numeric)
::: {.output .stream .stdout}
age Symptoms Steps Sleep height
count 450.000000 450.000000 450.000000 450.000000 450.000000
mean 18.962222 5.640000 3513.837778 6.026667 167.693333
std 0.801388 1.215783 1493.563465 1.276549 1.676299
min 18.000000 4.000000 0.000000 4.000000 165.000000
25% 18.000000 5.000000 2397.500000 5.000000 166.000000
50% 19.000000 6.000000 4264.500000 6.000000 168.000000
75% 20.000000 6.000000 4611.750000 7.000000 169.000000
max 20.000000 8.000000 4999.000000 8.000000 170.000000
familyMembers BMI weight educationLevel_encoded \
count 450.000000 450.000000 450.000000 450.000000
mean 3.980000 19.602800 55.111111 1.493333
std 1.557238 1.196811 3.225195 1.259689
min 1.000000 17.301038 50.000000 0.000000
25% 3.000000 18.507766 52.000000 0.000000
50% 4.000000 19.723183 55.000000 1.000000
75% 5.000000 20.549887 58.000000 3.000000
max 6.000000 22.038567 60.000000 3.000000
mood_avg stress_avg
count 450.000000 450.000000
mean 2.660317 5.489841
std 1.440725 2.871302
min 0.738095 1.666667
25% 1.095238 2.071429
50% 2.500000 5.488095
75% 4.452381 8.922619
max 4.761905 9.380952 :::
# Display correlation matrix
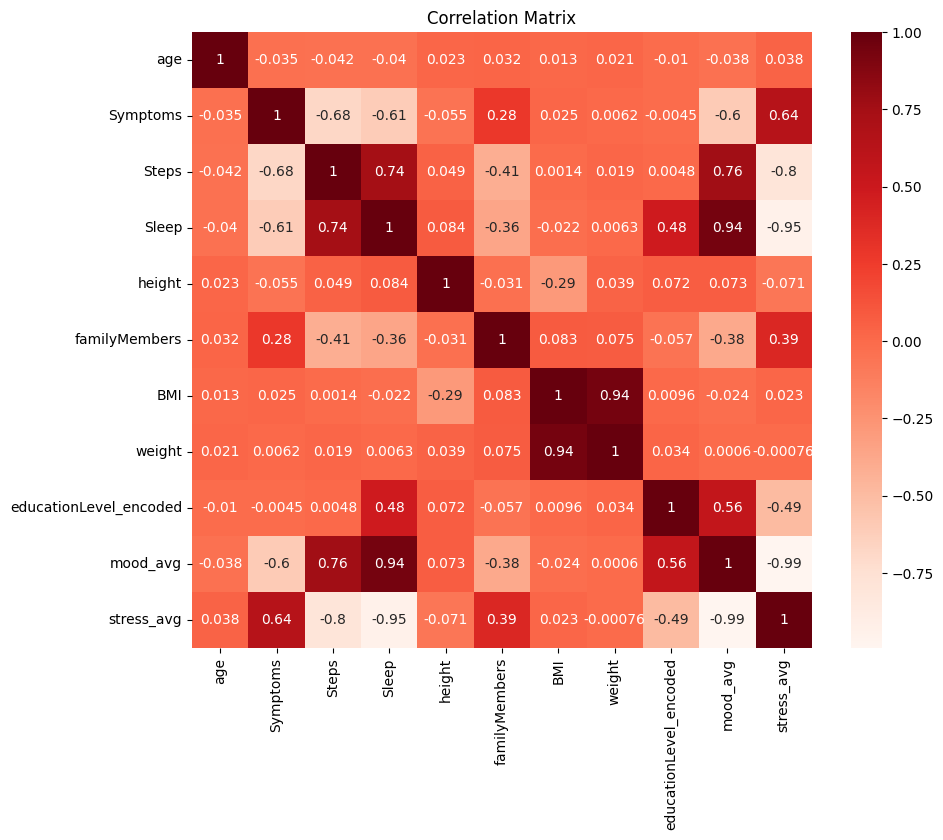
print(corr_matrix[['Steps', 'Sleep', 'mood_avg', 'stress_avg']])
::: {.output .stream .stdout} Steps Sleep mood_avg stress_avg age -0.042477 -0.040378 -0.037961 0.038342 Symptoms -0.676890 -0.609427 -0.603242 0.636993 Steps 1.000000 0.744269 0.759632 -0.800765 Sleep 0.744269 1.000000 0.943471 -0.945814 height 0.048546 0.083971 0.072506 -0.070950 familyMembers -0.410277 -0.358249 -0.384208 0.394963 BMI 0.001411 -0.022221 -0.023799 0.023282 weight 0.019262 0.006311 0.000597 -0.000760 educationLevel_encoded 0.004826 0.479324 0.559163 -0.492070 mood_avg 0.759632 0.943471 1.000000 -0.993244 stress_avg -0.800765 -0.945814 -0.993244 1.000000 :::
# Display catrgorized correlation matrix
print(corr_categories[['Steps', 'Sleep', 'mood_avg', 'stress_avg']])
::: {.output .stream .stdout}
Steps Sleep
age No correlation No correlation
Symptoms Moderately negative Moderately negative
Steps Very strongly positive Strongly positive
Sleep Strongly positive Very strongly positive
height No correlation No correlation
familyMembers Weakly negative Weakly negative
BMI No correlation No correlation
weight No correlation No correlation
educationLevel_encoded No correlation Weakly positive
mood_avg Strongly positive Very strongly positive
stress_avg Strongly negative Very strongly negative
mood_avg stress_avg
age No correlation No correlation
Symptoms Moderately negative Moderately positive
Steps Strongly positive Strongly negative
Sleep Very strongly positive Very strongly negative
height No correlation No correlation
familyMembers Weakly negative Weakly positive
BMI No correlation No correlation
weight No correlation No correlation
educationLevel_encoded Moderately positive Weakly negative
mood_avg Very strongly positive Very strongly negative
stress_avg Very strongly negative Very strongly positive :::
Heatmap for visualization of correlation matrix
import seaborn as sns
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import seaborn as sns
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.figure(figsize=(10,8)) # Set the figure size
sns.heatmap(corr_matrix, annot=True, cmap=plt.cm.Reds)
plt.title("Correlation Matrix")
plt.show()
::: {.output .display_data}
 :::
:::
Pairplot for visualization of correlation matrix
import pandas as pd
import seaborn as sns
# Create a new figure and set the title
plt.figure(figsize=(8, 8))
plt.suptitle("Correlogram of Correlation Matrix")
# Use the Seaborn library to draw a grid of scatterplots
sns.set(style="white")
sns.pairplot(df, diag_kind="hist", corner=True)
::: {.output .display_data}
 :::
:::
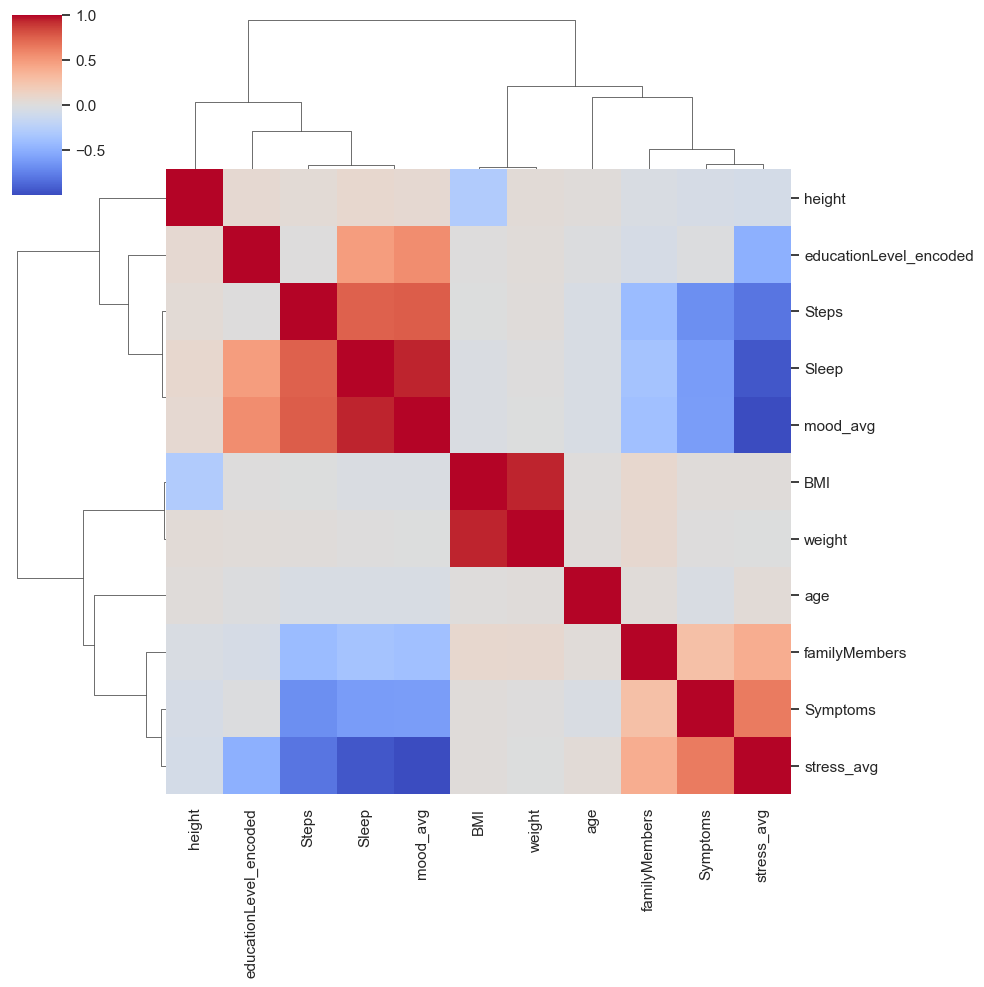
import scipy.cluster.hierarchy as sch
import seaborn as sns
# Compute hierarchical clustering
d = sch.distance.pdist(corr_matrix)
L = sch.linkage(d, method='complete')
# Plot dendrogram using seaborn
sns.clustermap(corr_matrix, method='complete', metric='correlation', figsize=(10,10), cmap='coolwarm')
 :::
:::
Pairwise correlation between two variables (numeric and non-numeric)
import pandas as pd
# create example DataFrame
data = {'educationLevel': df['educationLevel'],'mood': df['mood']}
df2 = pd.DataFrame(data)
# flatten the mood column using the explode() method
df2 = df2.explode('mood')
# convert the mood column to numeric
df2['mood'] = pd.to_numeric(df2['mood'])
# manually assign numerical codes for educationLevel
edu_dict = {'high school': 0, 'Secondary': 1, 'Post-sec': 2, 'Bachelors': 3,
'master': 4, 'Doctorate': 5, 'Others':7}
# calculate the correlation between educationLevel and mood
corr2 = df2['educationLevel'].astype('category').cat.codes.corr(df2['mood'], method='pearson')
codes = df2['educationLevel'].unique()
print(codes)
print('The correlation between Education Level and mood is : ', categorize_correlation(corr2), "(", corr2 , ")")
::: {.output .stream .stdout} [‘Secondary’ ‘Doctorate’ ‘Bachelors’ ‘Masters’] The correlation between Education Level and mood is : Moderately positive ( 0.5137839477571693 ) :::
import pandas as pd
# create example DataFrame
data = {'ethnicity': df['ethnicity'],'mood_avg': df_numeric['mood_avg']}
df3 = pd.DataFrame(data)
# flatten the mood column using the explode() method
#df3 = df3.explode('mood')
# convert the mood column to numeric
df3['mood_avg'] = pd.to_numeric(df3['mood_avg'])
# calculate the correlation between educationLevel and mood
corr3 = df3['ethnicity'].astype('category').cat.codes.corr(df3['mood_avg'], method='spearman')
codes3 = df3['ethnicity'].astype('category').unique()
print(codes3)
print('The correlation between Ethnicity and mood is : ', categorize_correlation(corr3), "(", corr3 , ")")
::: {.output .stream .stdout} [‘Japanese’, ‘Indian’, ‘Chinese’, ‘Danish’] Categories (4, object): [‘Chinese’, ‘Danish’, ‘Indian’, ‘Japanese’] The correlation between Ethnicity and mood is : Weakly positive ( 0.372509752920904 ) :::
import pandas as pd
# create example DataFrame
data = {'industry': df['industry'],'stress': df['stress']}
df4 = pd.DataFrame(data)
# flatten the mood column using the explode() method
df4 = df4.explode('stress')
# convert the mood column to numeric
df4['stress'] = pd.to_numeric(df4['stress'])
# calculate the correlation between educationLevel and mood
corr4 = df4['industry'].astype('category').cat.codes.corr(df4['stress'])
codes4 = df4['industry'].astype('category').unique()
print(codes4)
print('The correlation between Working industry and stress is : ', categorize_correlation(corr4),"(", corr4 , ")")
::: {.output .stream .stdout} [‘Technology’, ‘Finance’, ‘F&B’, ‘Aerospace’, ‘Healthcare’, ‘Student’] Categories (6, object): [‘Aerospace’, ‘F&B’, ‘Finance’, ‘Healthcare’, ‘Student’, ‘Technology’] The correlation between Working industry and stress is : No correlation ( -0.07978985123910241 ) :::
import pandas as pd
# create example DataFrame
data = {'maritialStatus': df['maritialStatus'],'stress': df['stress']}
df5 = pd.DataFrame(data)
# flatten the mood column using the explode() method
df5 = df5.explode('stress')
# convert the mood column to numeric
df5['stress'] = pd.to_numeric(df5['stress'])
# calculate the correlation between educationLevel and mood
corr5 = df5['maritialStatus'].astype('category').cat.codes.corr(df5['stress'])
codes5 = df5['maritialStatus'].astype('category').unique()
print(codes5)
print('The correlation between maritial status and stress is : ', categorize_correlation(corr5), "(", corr5 , ")")
::: {.output .stream .stdout} [‘Separated’, ‘Single’, ‘Divorced’] Categories (3, object): [‘Divorced’, ‘Separated’, ‘Single’] The correlation between maritial status and stress is : No correlation ( 0.05494827379728323 ) :::
# extract the features and targets
x = df_numeric[['age', 'Symptoms', 'Steps', 'Sleep', 'height', 'familyMembers', 'BMI', 'weight']]
y = df_numeric[['stress','mood']]
print(y.head(1))
df_numeric['mood_avg'] = df_numeric['mood'].apply(lambda x: np.mean(x))
df_numeric['stress_avg'] = df_numeric['stress'].apply(lambda x: np.mean(x))
print(df_numeric['stress_avg'].head(1))
print(df_numeric['mood_avg'].head(1))
::: {.output .stream .stdout}
stress
0 [1, 1, 3, 3, 1, 1, 1, 1, 2, 3, 3, 2, 2, 3, 1, …
mood
0 [4, 5, 4, 4, 5, 4, 5, 5, 4, 4, 5, 5, 5, 4, 4, ...
0 1.738095
Name: stress_avg, dtype: float64
0 4.571429
Name: mood_avg, dtype: float64 :::
Testing and evaluating Linear Regression and Random Forest Regression Features: Personal particulars of users Target variable (prediction): Average mood level and average stress level
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestRegressor
from sklearn.metrics import mean_squared_error, r2_score, mean_absolute_error
from sklearn.svm import SVR
# read data from the provided data structure
# extract the features and targets
x = df_numeric[[ 'Symptoms', 'Steps', 'Sleep', 'BMI']]
y = df_numeric[['stress','mood']]
# flatten the nested lists in the 'stress' and 'mood' columns
y = y.apply(lambda x: pd.Series(x.values[0]), axis=1)
# split the data into training and testing sets
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(x, y, test_size=0.4, train_size=0.6)
# create a linear regression model and fit it to the training data
model_LR = LinearRegression()
model_LR.fit(X_train, y_train)
y_pred_LR = model_LR.predict(X_test)
model_RF = RandomForestRegressor(n_estimators=100)
model_RF.fit(X_train, y_train)
y_pred_RF = model_RF.predict(X_test)
# Calculate metrics for linear regression
rmse_LR = np.sqrt(mean_squared_error(y_test, y_pred_LR))
mae_LR = mean_absolute_error(y_test, y_pred_LR)
mse_LR = mean_squared_error(y_test, y_pred_LR)
rsq_LR = r2_score(y_test, y_pred_LR)
# Calculate metrics for random forest
rmse_RF = np.sqrt(mean_squared_error(y_test, y_pred_RF))
mae_RF = mean_absolute_error(y_test, y_pred_RF)
mse_RF = mean_squared_error(y_test, y_pred_RF)
r2_RF = r2_score(y_test, y_pred_RF)
#print metrics for linear regression
print("LINEAR REGRESSION")
print("RMSE_LR:", rmse_LR)
print("Mean Absolute Error (MAE):", mae_LR)
print("Mean Squared Error (MSE):", mse_LR)
print("R-squared_LR:", rsq_LR)
# Print metrics for random forest
print("RANDOM FOREST")
print("RMSE_RF:", rmse_RF)
print("Mean Absolute Error (MAE):", mae_RF)
print("Mean Squared Error (MSE):", mse_RF)
print("R² score:", r2_RF)
::: {.output .stream .stdout} LINEAR REGRESSION RMSE_LR: 1.2787902846996444 Mean Absolute Error (MAE): 1.062966702293544 Mean Squared Error (MSE): 1.6353045922421974 R-squared_LR: 0.8248783260964155 RANDOM FOREST RMSE_RF: 0.9858273926748782 Mean Absolute Error (MAE): 0.8326944444444441 Mean Squared Error (MSE): 0.9718556481481484 R² score: 0.8958247847078721 :::
# extract the features and targets
x = df_numeric[['age', 'Symptoms', 'Steps', 'Sleep', 'height', 'familyMembers', 'BMI', 'weight']]
y = df_numeric[['stress_avg', 'mood_avg']]
# split the data into training and testing sets
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(x, y, test_size=0.4, train_size=0.6)
# create a linear regression model and fit it to the training data
model_LR = LinearRegression()
model_LR.fit(X_train, y_train)
y_pred_LR = model_LR.predict(X_test)
model_RF = RandomForestRegressor(n_estimators=100)
model_RF.fit(X_train, y_train)
y_pred_RF = model_RF.predict(X_test)
# Calculate metrics for linear regression
rmse_LR = np.sqrt(mean_squared_error(y_test, y_pred_LR))
mae_LR = mean_absolute_error(y_test, y_pred_LR)
mse_LR = mean_squared_error(y_test, y_pred_LR)
rsq_LR = r2_score(y_test, y_pred_LR)
# Calculate metrics for random forest
rmse_RF = np.sqrt(mean_squared_error(y_test, y_pred_RF))
mae_RF = mean_absolute_error(y_test, y_pred_RF)
mse_RF = mean_squared_error(y_test, y_pred_RF)
r2_RF = r2_score(y_test, y_pred_RF)
#print metrics for linear regression
print("LINEAR REGRESSION")
print("RMSE_LR:", rmse_LR)
print("Mean Absolute Error (MAE):", mae_LR)
print("Mean Squared Error (MSE):", mse_LR)
print("R-squared_LR:", rsq_LR)
# Print metrics for random forest
print("RANDOM FOREST")
print("RMSE_RF:", rmse_RF)
print("Mean Absolute Error (MAE):", mae_RF)
print("Mean Squared Error (MSE):", mse_RF)
print("R² score:", r2_RF)
::: {.output .stream .stdout} LINEAR REGRESSION RMSE_LR: 0.6730550163766352 Mean Absolute Error (MAE): 0.5476575960312353 Mean Squared Error (MSE): 0.45300305506975275 R-squared_LR: 0.9065703476800329 RANDOM FOREST RMSE_RF: 0.12466047805282841 Mean Absolute Error (MAE): 0.09757870370370339 Mean Squared Error (MSE): 0.015540234788359714 R² score: 0.9966030656257614 :::
After converting non-numeric values to numeric values
# extract the features and targets
x = df_encoded[[
'age' ,
'Symptoms' ,
'Steps' ,
'Sleep' ,
'height' ,
'familyMembers' ,
'BMI' ,
'weight' ,
'educationLevel_encoded',
'gender_F' ,
'gender_M' ,
'industry_Aerospace' ,
'industry_F&B' ,
'industry_Finance' ,
'industry_Healthcare' ,
'industry_Student' ,
'industry_Technology' ,
'ethnicity_Chinese' ,
'ethnicity_Danish' ,
'ethnicity_Indian' ,
'ethnicity_Japanese' ,
'nationality_Chinese' ,
'mentalIllness_None' ,
'livingArea_U' ]]
df_encoded['mood_avg'] = df_encoded['mood'].apply(lambda x: np.mean(x))
df_encoded['stress_avg'] = df_encoded['stress'].apply(lambda x: np.mean(x))
y = df_encoded[['stress_avg', 'mood_avg']]
# split the data into training and testing sets
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(x, y, test_size=0.4, train_size=0.6)
# create a linear regression model and fit it to the training data
model_LR = LinearRegression()
model_LR.fit(X_train, y_train)
y_pred_LR = model_LR.predict(X_test)
model_RF = RandomForestRegressor(n_estimators=100)
model_RF.fit(X_train, y_train)
y_pred_RF = model_RF.predict(X_test)
# Calculate metrics for linear regression
rmse_LR = np.sqrt(mean_squared_error(y_test, y_pred_LR))
mae_LR = mean_absolute_error(y_test, y_pred_LR)
mse_LR = mean_squared_error(y_test, y_pred_LR)
rsq_LR = r2_score(y_test, y_pred_LR)
# Calculate metrics for random forest
rmse_RF = np.sqrt(mean_squared_error(y_test, y_pred_RF))
mae_RF = mean_absolute_error(y_test, y_pred_RF)
mse_RF = mean_squared_error(y_test, y_pred_RF)
r2_RF = r2_score(y_test, y_pred_RF)
#print metrics for linear regression
print("LINEAR REGRESSION")
print("RMSE_LR:", rmse_LR)
print("Mean Absolute Error (MAE):", mae_LR)
print("Mean Squared Error (MSE):", mse_LR)
print("R-squared_LR:", rsq_LR)
# Print metrics for random forest
print("RANDOM FOREST")
print("RMSE_RF:", rmse_RF)
print("Mean Absolute Error (MAE):", mae_RF)
print("Mean Squared Error (MSE):", mse_RF)
print("R² score:", r2_RF)
::: {.output .stream .stdout} LINEAR REGRESSION RMSE_LR: 0.12590361863227206 Mean Absolute Error (MAE): 0.09984682525271399 Mean Squared Error (MSE): 0.015851721184700605 R-squared_LR: 0.9964570662002197 RANDOM FOREST RMSE_RF: 0.12962421460453175 Mean Absolute Error (MAE): 0.10219973544973526 Mean Squared Error (MSE): 0.0168024370118417 R² score: 0.996381272053682 ::: :::